
The difference between stepper motor and servo motor are listed below: What is the difference between a stepper motor and a servo motor? The feedback from the motor is used by the servo motor control loop, which helps the motor to reach the desired velocity and position.The output shaft of the servo motor can be moved to a specific velocity, position, and angle while regular motors cannot.The difference between regular motor and servo motor are listed below: What is the difference between a regular motor and a servo motor?

But, using 12 to 23 motors on the Mega board can disable the PWM functionality on the pin number 11 and 12. It means we can use 12 motors on Arduino Mega. The use of motors on Mega is also limited. On other Arduino boards, the servo library disables the PWM pin 9 and 10 even if the servo is connected to these pins.

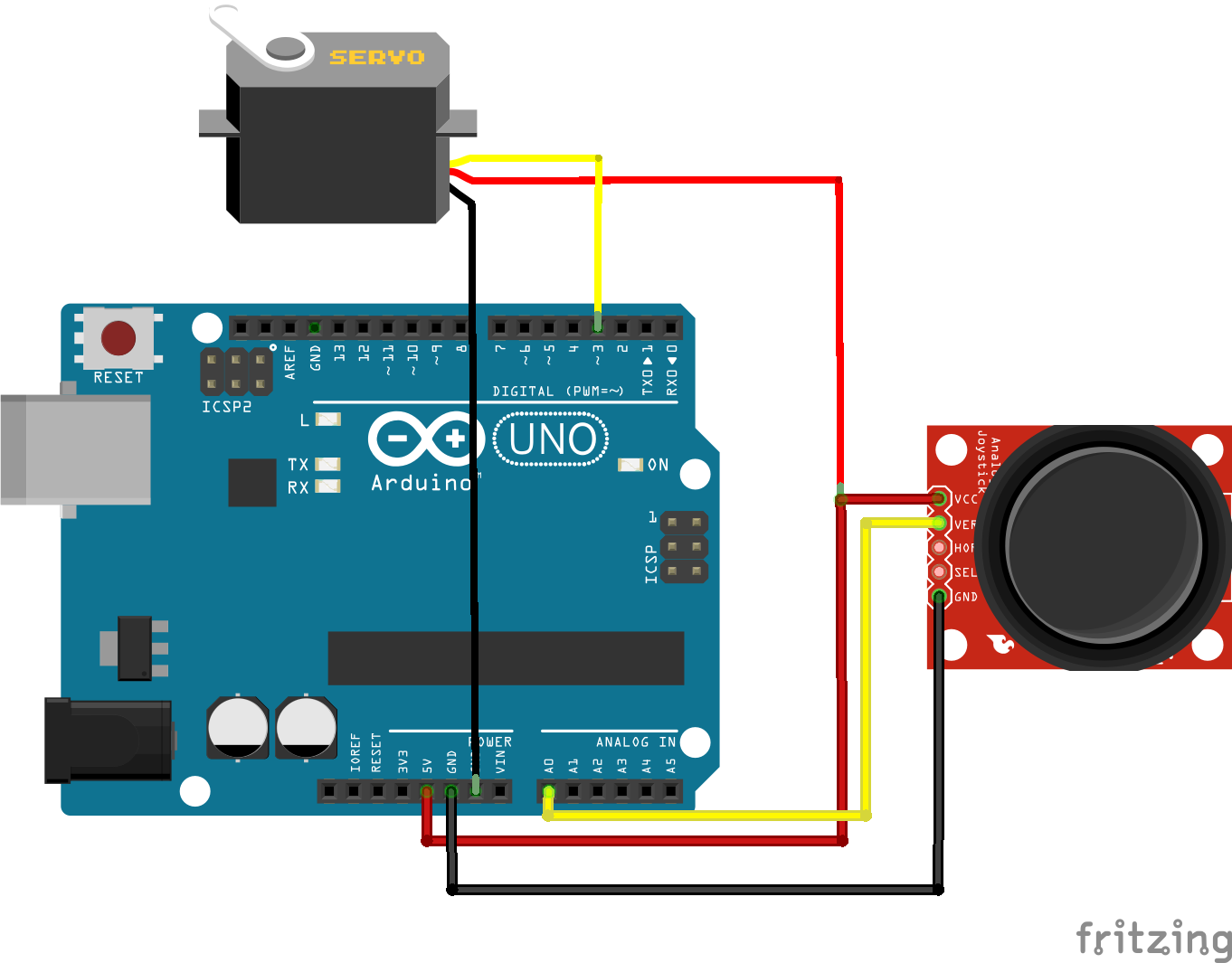
It is because servos do not interfere with the functionality of PWM pins on the Arduino Mega board. The servo library on Arduino boards can support upto 12 motors, while on Arduino Mega board, it can support upto 48 motors. We can also position shaft at different angles between 0 and 180 degrees. The servo library allows controlling the integrated shaft and gears. What is the Servo library, and why is it used? The Servo library is the library that permits the Arduino to work with servo motors. The movement in a servo motor is determined by an electric signal that can be either digital or analog. The controller is considered as an essential part of the servo motor. The applications of servo motors are machinery, automated manufacturing, robotics, radio controller airplanes, etc. The advantages of a servo motor are listed below: It has closed-loop feedback for controlling the torque and speed. It means that it has a rotor, stator, and control assemblies. The construction of the servo motor is similar to a DC motor. It means that the duration of pulses applied to the specific control pin controls the angle of rotation of the motor. The principle of the servo motor is based on Pulse Width modulation (PWM).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
